
로켓 추진제 및 연료 분류

화학 추진제

액체 추진제

액체 산소(LOX) / 액체 수소(LH2)
Liquid Oxygen(LOX, 액체산소)


액체수소(液體水素,liquid hydrogen)



LOX / RP-1 (로켓 추진제-1)
RP-1은 로켓연료로 사용되는 고도로 정제된 무독성의 등유를 말한다.

하이퍼골릭(예: 히드라진/사산화질소)
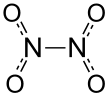
사산화 이질소는 강한 독성과 부식성을 가진 강력한 산화제이다. N2O4는 다양한 형태의 하이드라진을 지닌 자동점화성 추진제이다.

고체 추진제

복합 추진제(예: 과염소산암모늄 복합 추진제 - APCP)
APCP: 과염소산 암모늄을 산화제로 쓰는 복합 추진제입니다. 우주왕복선의 고체 로켓 부스터에 쓰였던 추진제



이중 기반 추진제(예: 니트로글리세린 및 니트로셀룰로오스)
니트로셀룰로오스 화약에는 β-화약과 피로콜로디온(pyrocollodion)화약이 있으며, 니트로글리세린 화약에는 가루형, 구형, 관형 등이 있고, 주로 탄환의 발사약으로 사용되나 로켓 발사약으로 사용되기도 한다.
하이브리드 추진제
액체 산화제 및 고체 연료(예: LOX/HTPB - 하이드록실 말단 폴리부타디엔)
비화학 추진제
전기 추진
전열(예: Resistojets, Arcjets)
정전기(예: 이온 추진기)
전자기(예: 홀 효과 추진기)
핵추진
핵열추진(NTP)
원자력 전기 추진(NEP)
장단점 분석
액체 추진제
LOX/LH2
장점:
높은 비충격(Isp)으로 효율적인 추진력 제공.
수소는 가벼워 성능이 향상됩니다.
단점:
극저온 보관이 필요하므로 복잡성과 무게가 추가됩니다.
수소는 밀도가 낮아 연료탱크가 크다.
LOX/RP-1
장점:
높은 에너지 밀도로 우수한 성능을 제공합니다.
극저온 연료에 비해 취급 및 보관이 더 쉽습니다.
단점:
LOX/LH2에 비해 Isp가 낮습니다.
엔진과 광학 장치를 오염시킬 수 있는 그을음이 더 많이 생성됩니다.
하이퍼골릭
장점:
접촉 시 점화되어 엔진 설계 및 신뢰성이 단순화됩니다.
주변 온도에서 보관 가능하며 장기간 임무에 이상적입니다.
단점:
독성이 강하고 발암성이 있어 안전에 위험이 있습니다.
극저온 추진제에 비해 성능이 낮습니다.
고체 추진제
복합 추진제(예: APCP)
장점:
움직이는 부품이 없는 심플한 디자인으로 신뢰성이 향상되었습니다.
높은 추력 대 중량 비율로 강력한 초기 가속력을 제공합니다.
단점:
한번 점화되면 조절하거나 종료할 수 없습니다.
액체 추진제에 비해 Isp가 낮습니다.
이중 추진제
장점:
균일한 혼합물로 균일한 성능을 제공합니다.
복합 추진제보다 밀도가 높습니다.
단점:
온도와 기계적 충격에 민감합니다.
일반적으로 고급 복합 추진제보다 성능이 낮습니다.
하이브리드 추진제
LOX/HTPB
장점:
고체 추진제와 액체 추진제의 장점을 결합합니다.
액체 엔진처럼 조절하고 종료할 수 있습니다.
단점:
액체 및 고체 처리 시스템이 모두 필요한 복잡한 설계.
비행 유산 사례가 적고 덜 성숙한 기술입니다.
전기 추진
이온 추진기
장점:
매우 높은 Isp로 효율적인 장기 추력을 제공합니다.
추진제 소비가 적기 때문에 심우주 임무에 이상적입니다.
단점:
추력이 매우 낮아 빠른 기동이나 발사에는 적합하지 않습니다.
상당한 전력이 필요합니다.
홀 효과 추진기
장점:
추력과 효율성 사이의 균형이 잘 맞습니다.
우주에서 좋은 실적을 거둔 입증된 기술입니다.
단점:
상당한 전력 공급이 필요합니다.
시간이 지남에 따라 추진기 구성 요소가 침식됩니다.
핵 추진
핵열추진(NTP)
장점:
상당한 추진력을 갖춘 높은 Isp로 화성 유인 임무에 적합합니다.
심우주 임무의 이동 시간을 잠재적으로 줄일 수 있습니다.
단점:
복잡하고 비용이 많이 드는 개발.
원자력 안전에 대한 대중적, 정치적 우려.
원자력 전기 추진(NEP)
장점:
매우 높은 Isp로 장기간의 우주 임무에 이상적입니다.
추진제의 효율적인 사용.
단점:
대규모 발전 시스템이 필요합니다.
추력 수준이 낮아 기동성이 제한됩니다.
결론
각 유형의 로켓 추진제 및 연료에는 고유한 장점과 단점이 있으므로 다양한 응용 분야에 적합합니다. 액체 추진제는 고성능과 조절 기능을 제공하고, 고체 추진제는 단순성과 신뢰성을 제공하며, 하이브리드 추진제는 두 가지 장점을 결합하고, 전기 추진 시스템은 심우주 임무에 매우 효율적이며, 핵 추진제는 장기간 임무에 높은 성능을 제공합니다. 추진제의 선택은 추력 요구 사항, 지속 시간 및 운영 환경을 포함한 특정 임무 요구 사항에 따라 달라집니다.
Rocket propellants and fuels are classified based on their physical state (liquid, solid, hybrid), chemical composition (chemical, non-chemical), and their method of propulsion (chemical propulsion, electric propulsion, nuclear propulsion, etc.). Here's a detailed classification and analysis of the major types of rocket propellants and fuels:
### Classification of Rocket Propellants and Fuels
1. **Chemical Propellants**
- **Liquid Propellants**
- **Liquid Oxygen (LOX) / Liquid Hydrogen (LH2)**
- **LOX / RP-1 (Rocket Propellant-1)**
- **Hypergolics (e.g., Hydrazine / Nitrogen Tetroxide)**
- **Solid Propellants**
- **Composite Propellants (e.g., Ammonium Perchlorate Composite Propellant - APCP)**
- **Double-base Propellants (e.g., Nitroglycerin and Nitrocellulose)**
- **Hybrid Propellants**
- **Liquid oxidizer and solid fuel (e.g., LOX / HTPB - Hydroxyl-terminated polybutadiene)**
2. **Non-Chemical Propellants**
- **Electric Propulsion**
- **Electrothermal (e.g., Resistojets, Arcjets)**
- **Electrostatic (e.g., Ion Thrusters)**
- **Electromagnetic (e.g., Hall Effect Thrusters)**
- **Nuclear Propulsion**
- **Nuclear Thermal Propulsion (NTP)**
- **Nuclear Electric Propulsion (NEP)**
### Analysis of Pros and Cons
#### Liquid Propellants
- **LOX/LH2**
- **Pros:**
- High specific impulse (Isp), providing efficient propulsion.
- Hydrogen is lightweight, enhancing performance.
- **Cons:**
- Requires cryogenic storage, adding complexity and weight.
- Hydrogen has low density, leading to large fuel tanks.
- **LOX/RP-1**
- **Pros:**
- High energy density, offering good performance.
- Easier to handle and store than cryogenic fuels.
- **Cons:**
- Lower Isp compared to LOX/LH2.
- Produces more soot, which can contaminate engines and optics.
- **Hypergolics**
- **Pros:**
- Ignites on contact, simplifying engine design and reliability.
- Storable at ambient temperatures, ideal for long-duration missions.
- **Cons:**
- Highly toxic and carcinogenic, posing safety risks.
- Lower performance compared to cryogenic propellants.
#### Solid Propellants
- **Composite Propellants (e.g., APCP)**
- **Pros:**
- Simple design, with no moving parts, enhancing reliability.
- High thrust-to-weight ratio, providing strong initial acceleration.
- **Cons:**
- Once ignited, cannot be throttled or shut down.
- Lower Isp compared to liquid propellants.
- **Double-base Propellants**
- **Pros:**
- Homogeneous mixture, providing uniform performance.
- Higher density than composite propellants.
- **Cons:**
- Sensitive to temperature and mechanical shock.
- Typically lower performance than advanced composite propellants.
#### Hybrid Propellants
- **LOX/HTPB**
- **Pros:**
- Combines advantages of solid and liquid propellants.
- Can be throttled and shut down like liquid engines.
- **Cons:**
- Complex design, requiring both liquid and solid handling systems.
- Less mature technology with fewer flight heritage examples.
#### Electric Propulsion
- **Ion Thrusters**
- **Pros:**
- Extremely high Isp, providing efficient long-term thrust.
- Ideal for deep-space missions due to low propellant consumption.
- **Cons:**
- Very low thrust, unsuitable for rapid maneuvers or launch.
- Requires significant electrical power.
- **Hall Effect Thrusters**
- **Pros:**
- Good balance between thrust and efficiency.
- Proven technology with a good track record in space.
- **Cons:**
- Requires substantial power supply.
- Erosion of thruster components over time.
#### Nuclear Propulsion
- **Nuclear Thermal Propulsion (NTP)**
- **Pros:**
- High Isp with significant thrust, suitable for manned missions to Mars.
- Potentially reduces travel time for deep-space missions.
- **Cons:**
- Complex and costly development.
- Public and political concerns about nuclear safety.
- **Nuclear Electric Propulsion (NEP)**
- **Pros:**
- Extremely high Isp, ideal for long-duration deep-space missions.
- Efficient use of propellant.
- **Cons:**
- Requires large power generation systems.
- Low thrust levels, limiting maneuverability.
### Conclusion
Each type of rocket propellant and fuel has its own unique advantages and disadvantages, making them suitable for different applications. Liquid propellants offer high performance and throttling capability, solid propellants provide simplicity and reliability, hybrid propellants combine the benefits of both, electric propulsion systems are highly efficient for deep-space missions, and nuclear propulsion offers high performance for long-duration missions. The choice of propellant depends on the specific mission requirements, including thrust needs, duration, and operational environment.
'Memo' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 심사와 평가 (35) | 2024.08.01 |
|---|---|
| 도널드 트럼프 저격 시도 사건 (44) | 2024.07.17 |
| [개의 신호] 강아지 행동의 의미 (0) | 2024.06.25 |
| [개 꼬리의 의미] 강아지 꼬리의 의미 (1) | 2024.06.25 |
| [영화] 스타워즈 연대기 별 관람 순서 (0) | 2024.06.10 |